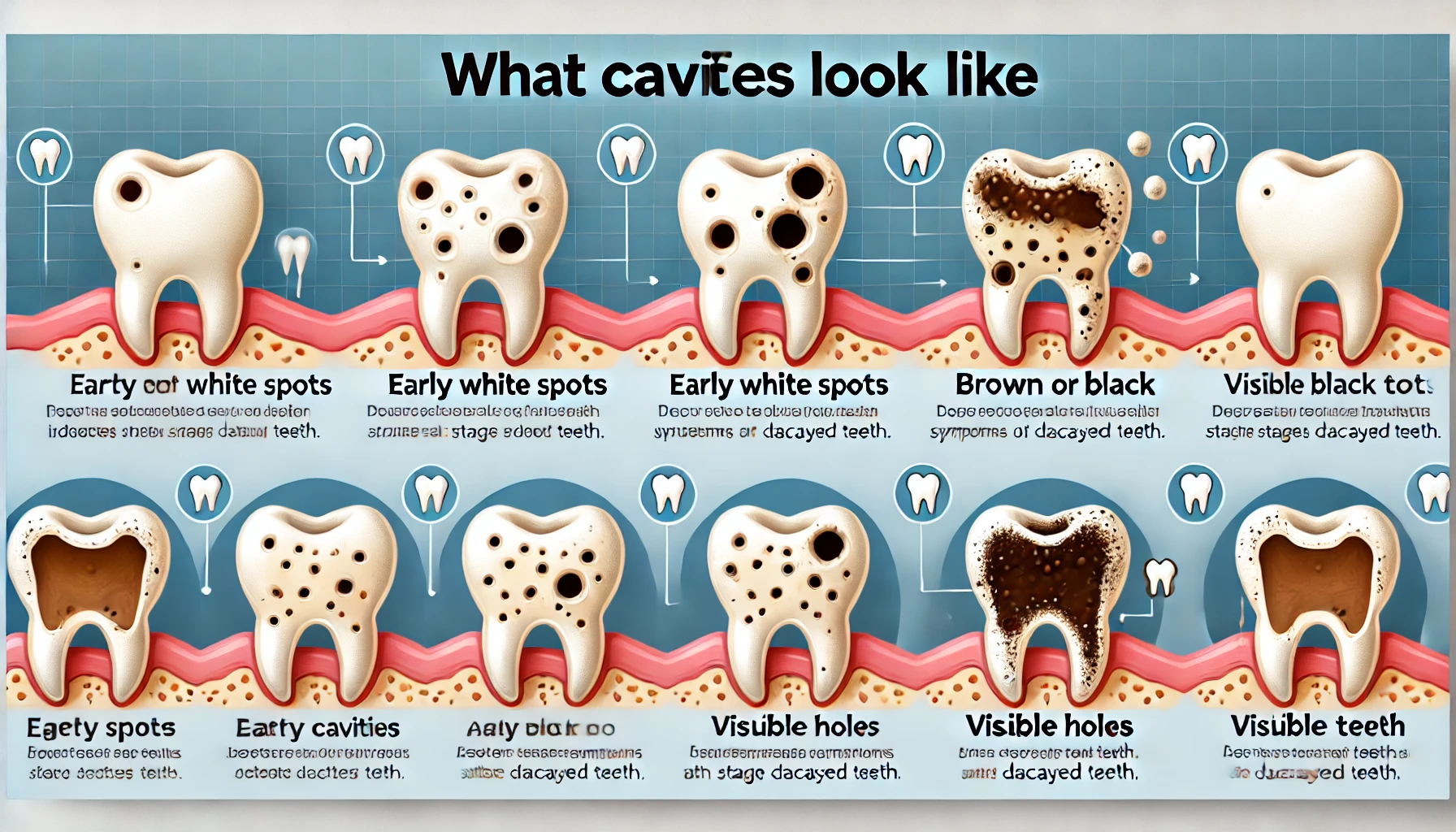
What Do Cavities Look Like? Understanding Dental Decay
Cavities, also known as dental caries or tooth decay, are one of the most common dental problems faced by people of all ages. They occur when harmful bacteria in the mouth produce acids that erode the enamel, leading to holes or cavities in the teeth. Understanding what cavities look like, their symptoms, causes, and treatment options is essential for maintaining good oral health. In this blog, we’ll explore the visual characteristics of cavities, how to recognize them, and what you can do to prevent and treat them.
1. Visual Signs of Cavities
Cavities can appear in various forms depending on their severity and location. Here are some common visual characteristics of cavities:
Color Changes
- White Spots: The earliest sign of tooth decay often appears as white spots on the enamel. These spots indicate demineralization, where minerals are lost due to acid attack. At this stage, the damage may be reversible with proper care.
- Brown or Black Spots: As cavities progress, they may develop into brown or black spots on the tooth surface. This discoloration is usually a sign that the decay has advanced beyond the enamel and into the dentin, the layer beneath the enamel.
Holes or Pits
- Visible Holes: In more advanced stages of decay, cavities can form holes or pits in the teeth. These cavities can vary in size and may be easily noticeable, especially on chewing surfaces or between teeth.
Texture Changes
- Roughness: Cavities can create rough areas on the surface of the tooth. You might notice that a tooth feels different when you run your tongue over it, feeling uneven or jagged.
Location of Cavities
- On Chewing Surfaces: Cavities often occur on the chewing surfaces of molars where food particles can get trapped.
- Between Teeth: Interproximal cavities form between teeth and can be difficult to detect without dental X-rays or a professional examination.
2. Symptoms Associated with Cavities
In addition to the visible signs, cavities can cause various symptoms that indicate decay. These may include:
- Tooth Sensitivity: You might experience sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods and drinks as the cavity progresses.
- Pain or Discomfort: As decay advances, it may lead to toothache or discomfort, especially when biting or chewing.
- Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath (halitosis) can be a sign of dental decay, as bacteria in the mouth produce foul-smelling gases.
- Swelling or Inflammation: In some cases, cavities can lead to swollen gums or inflammation around the affected tooth.
3. Causes of Cavities
Understanding what causes cavities can help in their prevention. The primary factors include:
Bacteria and Plaque
- Bacteria: The mouth is home to various bacteria, some of which produce acids that attack tooth enamel. When sugars from food are consumed, these bacteria thrive and produce more acid.
- Plaque Formation: When bacteria, food particles, and saliva combine, they form a sticky film known as plaque. If not removed through brushing and flossing, plaque hardens into tartar, which can lead to cavities.
Dietary Factors
- Sugary Foods and Drinks: High-sugar diets contribute significantly to the development of cavities. Foods like candies, sodas, and pastries provide fuel for bacteria.
- Frequent Snacking: Snacking throughout the day without proper oral hygiene can lead to constant acid production, increasing the risk of cavities.
Poor Oral Hygiene
- Inadequate Brushing and Flossing: Neglecting to brush and floss regularly allows plaque and bacteria to accumulate, raising the risk of decay.
Fluoride Deficiency
- Lack of Fluoride: Fluoride is essential for strengthening tooth enamel and making it more resistant to acid attacks. A deficiency can increase the likelihood of cavities.
4. Diagnosis of Cavities
Cavities are typically diagnosed during routine dental check-ups. Dentists use the following methods to identify cavities:
- Visual Examination: Dentists will visually inspect your teeth for signs of decay, discoloration, or holes.
- Dental X-rays: X-rays help in detecting cavities that may not be visible to the naked eye, especially between teeth or under existing fillings.
5. Treatment Options for Cavities
The treatment for cavities depends on their severity:
Fluoride Treatments
- Early Stage: If a cavity is detected early, fluoride treatments can help remineralize the enamel and reverse minor decay.
Fillings
- Moderate to Severe Cavities: If a cavity has progressed beyond the early stage, a dentist will remove the decayed portion of the tooth and fill it with a dental material (such as composite resin, amalgam, or glass ionomer).
Crowns
- Severe Decay: For extensive decay that weakens the tooth structure, a crown may be necessary to restore the tooth’s shape and function.
Root Canals
- Advanced Decay: If decay has reached the pulp of the tooth, a root canal may be required to remove infected tissue and save the tooth.
Extractions
- Severe Damage: In cases where the tooth is beyond repair, extraction may be the only option.
6. Prevention of Cavities
Preventing cavities is crucial for maintaining good oral health. Here are effective preventive measures:
- Regular Brushing and Flossing: Brush at least twice a day and floss daily to remove plaque and food particles.
- Routine Dental Check-ups: Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and professional cleanings to catch cavities early.
- Limit Sugary Foods: Reduce your intake of sugary snacks and beverages to minimize acid production.
- Use Fluoride Toothpaste: Fluoride strengthens enamel and helps protect against cavities.
- Consider Dental Sealants: Sealants can provide an additional layer of protection for the chewing surfaces of molars.
Conclusion
Cavities can significantly impact oral health, but understanding what they look like and recognizing their symptoms can lead to early detection and treatment. By maintaining good oral hygiene, making informed dietary choices, and regularly visiting your dentist, you can reduce your risk of developing cavities and keep your smile healthy for years to come. Remember, prevention is always better than cure, so take care of your teeth to enjoy a lifetime of good health!